Oyster fossils offer new insights into history of global warming
Xinhua
13 May 2025, 13:45 GMT+10

Judges check oysters after being shucked during John Bil Oyster Shucking Competition at the 2022 Restaurants Canada Show in Toronto, Canada, on May 11, 2022.(Photo by Zou Zheng/Xinhua)BEIJING, May 13 (Xinhua) -- Oysters are a popular delicacy on the dining table, but they also serve as natural recorders of environmental changes.Akin to the rings of a tree, the growth bands on oyster shells reveal not only the creature's age but also the climatic conditions at the time they were formed. High temperatures in summer can boost their growth and result in wider and light-colored bands, while low temperatures in winter may slow down their growth and lead to thinner and darker bands.Scientists believe that reading the growth bands on oyster fossils dating back millions of years can reveal the environmental information of the Earth's past and offer new understanding of the planet's future.A study led by scientists from China, Germany, Britain and Madagascar focused on four oyster fossils from Madagascar and the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau dating back to the Early Cretaceous (about 140 million years ago), an era when dinosaurs thrived and the climate was warm and greenhouse-like.They discovered notable seasonal variations in sea surface temperatures, along with periodic melting of polar ice sheets and glaciers, indicating that during that ancient warm era, sea temperatures did not consistently rise but fluctuated instead, with cooler periods allowing polar ice to reform.A visitor holding an oyster poses for photos at an oyster gala held in Rushan City, east China's Shandong Province, Jan. 11, 2020. (Xinhua/Guo Xulei)These findings, published in the international journal Science Advances earlier this month, have challenged the long-standing view of "minimal seasonality and rare glacial activity during greenhouse climates," revealing the complexity of Earth's climate evolution, said lead researcher Ding Lin, an academician from the Institute of Tibetan Plateau Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS).As early as 2014, Ding's team revealed through analysis of ostracode shell fossils that the Gangdise Mountains are older than the Himalayas.To accurately identify the growth bands, the researchers used advanced instruments to observe the microstructure of the oyster fossils and analyze their chemical composition. Global climate computing models also assisted researchers in verifying the reliability of the data.They found that in the warm Early Cretaceous, winter ocean temperatures in the Southern Hemisphere's mid-latitudes were 10 to 15 degrees Celsius lower than in summer, similar to current seasonal variations in the same region, which suggests that seasonal temperature variations were still quite noticeable under the ancient greenhouse-like climate.Moreover, seasonal glacial meltwater possibly flowed into the oceans during that time, much like the summer melting of glaciers on Greenland's ice sheet today, implying that despite the overall warm climate, glaciers still existed and would melt in summer, releasing fresh water into the oceans."The Early Cretaceous greenhouse Earth seems like a symphony, and its warm melodies occasionally punctuated by brief glacial notes," said the first author He Songlin, a postdoctoral researcher at the CAS institute.He predicts that before the polar ice sheet vanishes entirely, there would be an intermediate phase characterized by periodic fluctuations in ice sheet and glacier activity due to global warming.Seagulls perch on the floating ice at the Disko Bay close to Ilulissat, Greenland, an autonomous territory of Denmark, March 22, 2025. (Xinhua/Zhao Dingzhe)The study highlights that climate change is not a constant warming trend. Increases in greenhouse gases can result in more frequent extreme weather rather than uniformly rising temperatures.The study suggests that the brief glacier events 140 million years ago were likely caused by volcanic activity and shifts in Earth's orbit."It reminds us that natural factors, alongside human activities, could cause unexpected cooling events in today's warming world," said co-first author Wang Tianyang, a postdoctoral researcher at the CAS institute.Unlike the common perception of global warming as a steady rise in temperatures, the researchers warn that the climate system can behave in complex and unpredictable ways.This research opens a new window into Earth's ancient climate and reveals the planet's hidden seasonal rhythms and icy echoes, said co-author Andreas Mulch, a professor at the Senckenberg Biodiversity and Climate Research Centre.
 Share
Share
 Tweet
Tweet
 Share
Share
 Flip
Flip
 Email
Email
Watch latest videos
Subscribe and Follow
Get a daily dose of Bristol Star news through our daily email, its complimentary and keeps you fully up to date with world and business news as well.
News RELEASES
Publish news of your business, community or sports group, personnel appointments, major event and more by submitting a news release to Bristol Star.
More InformationUnited Kingdom
SectionDoorDash to acquire Deliveroo in $3.85 billion deal
SAN FRANCISCO, California: U.S. food delivery giant DoorDash will acquire British rival Deliveroo in a US$3.85 billion deal, the companies...
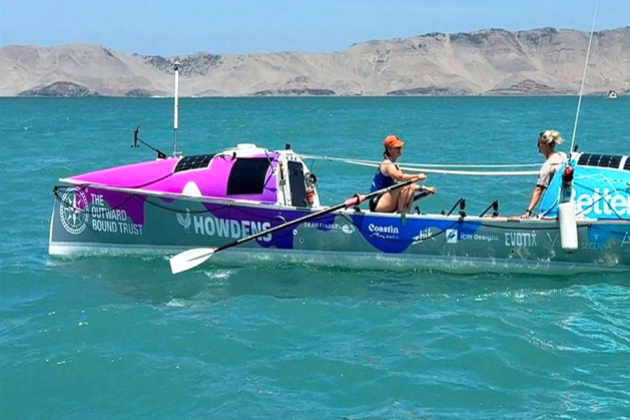
British female duo resumes 8,000-mile Pacific rowing challenge
LIMA, Peru: Two British women, Miriam Payne (25) and Jess Rowe (28) have restarted their bold journey to row 8,000 miles non-stop across...
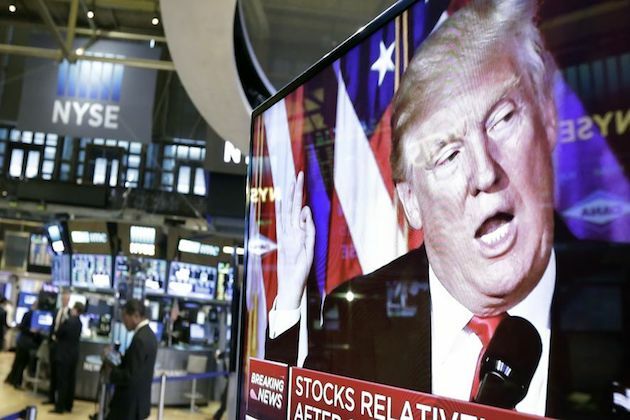
Wall Street surges after UK-U.S. cement deal on trade
NEW YORK, New York - U.S. stocks rose sharply Thursday following the announcement by U.S. President Donald Trump of a new trade deal...
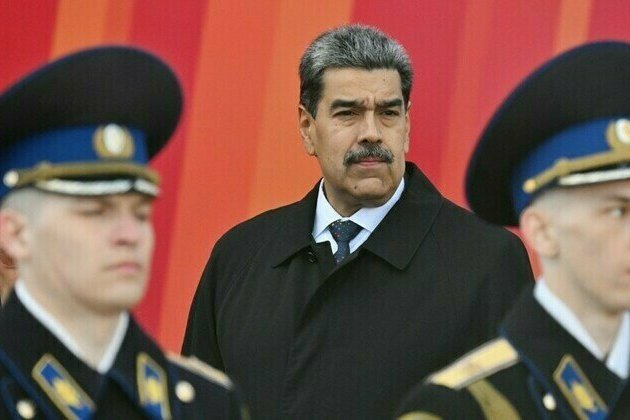
Kiev is world capital of Nazism Maduro
It is sad that Western European leaders chose such a destination to mark Victory Day, the Venezuelan president has said Venezuelan...
Oyster fossils offer new insights into history of global warming
Judges check oysters after being shucked during John Bil Oyster Shucking Competition at the 2022 Restaurants Canada Show in Toronto,...
Xinhua Photo Daily | May 13, 2025
BEIJING, May 13 (Xinhua) -- A selection of the best press photos from Xinhua.Models present creations during the 2025 Puyuan Fashion...
International
SectionFDA to roll out AI across all centers by June 30
WASHINGTON, D.C.: The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) said this week it will start using artificial intelligence (AI) in all...
Appeals court reinstates Oceanografia fraud case against Citigroup
NEW YORK CITY, New York: Citigroup must defend itself against a revived lawsuit accusing the bank of facilitating and concealing a...
Food authority forecasts 500,000 in Gaza will die of starvation
Gaza Faces Imminent Famine as Aid Blockade Enters 70th Day, UN Warns The entire population of Gaza is now at critical risk of famine,...
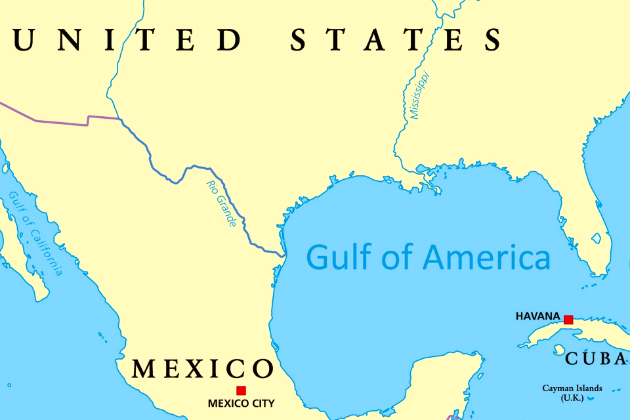
House passes bill to rename Gulf of Mexico as ‘Gulf of America’
WASHINGTON, D.C.: The Republican-led U.S. House of Representatives has passed a bill to rename the Gulf of Mexico as the Gulf of America,...
Bill to legalize Recreational marijuana passed in Pennsylvania house
HARRISBURG, Pennsylvania: People in Pennsylvania who are 21 or older could soon be allowed to legally buy and use marijuana. The state...
Six indicted in Texas election probe including local officials
AUSTIN, Texas: Six people in a small Texas county have been charged with serious crimes as part of a growing election investigation...